Artificial Intelligence (AI) is constantly pushing boundaries, and one of the most exciting advancements in recent years is the rise of AI agents. These intelligent systems go beyond traditional automation by performing complex tasks, making autonomous decisions, and learning from their environments. AI agents are poised to revolutionize industries by transforming how we interact with technology and manage operations.
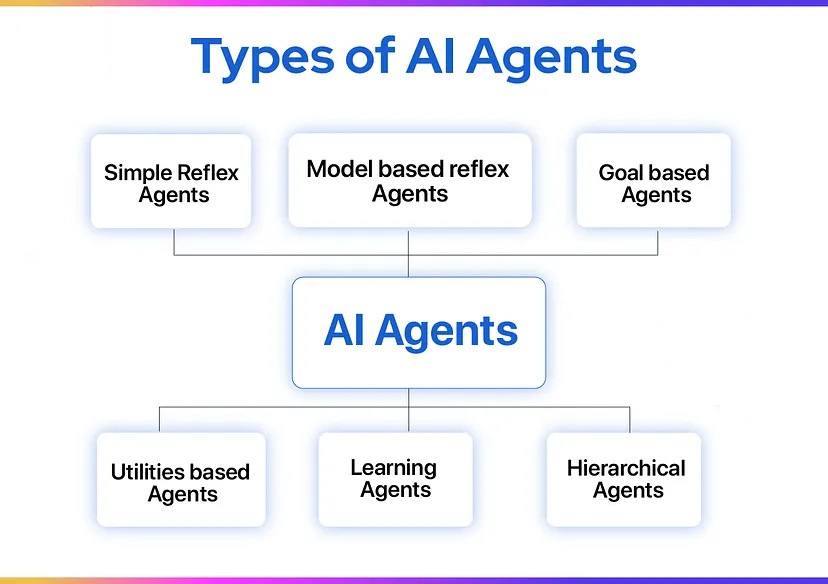
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are software entities capable of perceiving their environment, processing data, making decisions, and acting independently to achieve specific goals. They are designed to:
- Operate autonomously or semi-autonomously.
- Adapt to changing conditions through machine learning.
- Interact with humans, other systems, or even other AI agents.
From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to advanced AI-driven decision-making systems in industries, AI agents come in various forms, catering to diverse use cases.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents
1. Autonomy
AI agents can act independently without constant human supervision, enabling them to handle repetitive, complex, or time-sensitive tasks.
2. Proactive Behavior
Unlike traditional software that reacts to commands, AI agents can anticipate needs, make predictions, and take initiative.
3. Learning and Adaptability
AI agents use machine learning to adapt to new information or environments, improving their performance over time.
4. Collaboration
They can work collaboratively with humans or other systems, facilitating seamless operations and enhancing productivity.
Applications of AI Agents
1. Customer Service
AI agents, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, provide instant, 24/7 support to customers by resolving queries, offering product recommendations, and guiding users through processes.
2. Healthcare
AI agents assist in diagnostics, patient monitoring, and personalized treatment plans. For example, virtual agents analyze patient symptoms to recommend initial care steps.
3. Finance
In the financial sector, AI agents automate fraud detection, portfolio management, and real-time trading, making decisions based on vast datasets.
4. Education
AI agents serve as personalized tutors, helping students learn at their own pace while identifying areas for improvement.
5. Smart Homes and IoT
Virtual agents integrated into IoT devices manage home automation tasks like controlling appliances, optimizing energy usage, and ensuring security.
Benefits of AI Agents
1. Enhanced Efficiency
AI agents reduce the need for manual intervention, speeding up processes and minimizing errors.
2. Cost Savings
By automating routine tasks and improving resource management, AI agents lower operational costs for businesses.
3. Improved User Experience
AI agents offer personalized and proactive interactions, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement.
4. Scalability
AI agents can handle large-scale operations, making them indispensable for businesses aiming to expand without increasing costs proportionally.
Challenges in Adopting AI Agents
While the potential of AI agents is immense, there are challenges to address:
1. Ethical Concerns
Autonomous decision-making raises questions about accountability and fairness, particularly in sensitive applications like hiring or law enforcement.
2. Data Privacy and Security
AI agents rely on vast amounts of data, making it critical to safeguard sensitive information from breaches or misuse.
3. Skill Requirements
Organizations must invest in upskilling employees to work alongside AI agents effectively.
4. Bias in AI
AI agents can inherit biases from their training data, leading to unintended consequences. Developers must prioritize fairness and inclusivity during development.
The Future of AI Agents
The emergence of AI agents represents a shift toward autonomous ecosystems where machines and humans collaborate seamlessly. In the near future, we can expect:
- Greater Human-AI Collaboration: AI agents acting as co-workers, assisting in creative and decision-making processes.
- Self-Improving Agents: Continuous learning capabilities that allow agents to evolve and improve independently.
- Domain-Specific Expertise: AI agents tailored to industries like law, education, and medicine, delivering unparalleled expertise.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: Stricter guidelines to ensure responsible and equitable use of AI agents.
Conclusion
The emergence of AI agents is redefining the boundaries of automation and autonomy. By integrating these intelligent systems into our workflows and daily lives, we are paving the way for greater innovation, efficiency, and collaboration. However, as we embrace this transformative technology, it is crucial to address ethical, security, and inclusivity challenges to ensure that AI agents benefit society as a whole.
At [Your Website Name], we are committed to exploring and sharing insights about the latest advancements in AI. Stay tuned for more updates on how AI agents are shaping the future of work and life.
!DOCTYPE html>